Color Measurement of Food Dyes

Color is a critical sensory attribute of food products and can influence consumer perception, preference, and purchasing decisions. Therefore, many food products contain synthetic (artificial) or natural food dyes that enhance their visual appeal – from confections to beverages, baked goods, dairy products, snacks, etc. It is thus essential for the food industry to have an accurate color measurement of these food dyes.
Techniques for Measuring the Color of Food Dyes
The traditional way to measure the color of food dyes involves visually assessing them. However, this method is subjective, and the results can vary depending on the observer’s perception, the surrounding lighting conditions, etc. In addition, it is also rather difficult to reproduce the same assessment consistently across the samples. Unlike the visual color assessment method, instrumental color measurement provides quantitative data, making it easier to compare color measurements or to identify subtle color or shade changes. This method involves the use of color measurement devices such as a spectrophotometer to measure the light reflected or transmitted by the sample to generate its spectral data. The data is then processed to calculate color values based on established color spaces like CIE L*a*b* or CIE L*C*h.
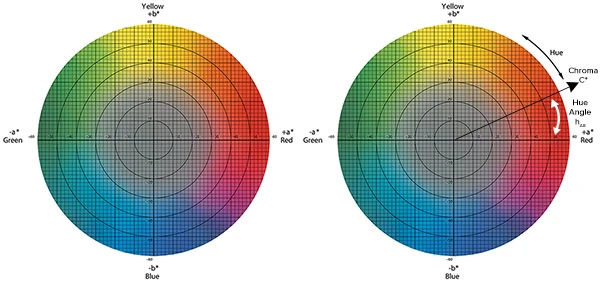
CIE L*a*b* (left) and CIE L*C*h (right).
Food Dyes Color Measurement with Spectrophotometer
Spectrophotometers, widely used in the food industry, have a variety of applications for the color measurement of food dyes. They can support the formulation of food dyes by measuring the color properties of different dyes and additives to identify the best combination of ingredients for achieving the desired color. Spectrophotometers can be used to verify if the food dyes from the suppliers meet the required color specifications before being incorporated into food products. They are also useful in color quality control between different stages of production by identifying any color variations that may occur during the production process. Additionally, spectrophotometers can be utilized to monitor the color stability of food dyes over time, especially when exposed to light, heat, etc., and is helpful for understanding the shelf life and storage requirements of food dyes.
As spectrophotometers come in various measurement modes, e.g., reflectance or transmittance, that are designed to measure different types of samples, it is, therefore, crucial to use the appropriate measurement mode to ensure the color of the food dyes is accurately measured. For example, reflectance color measurement mode is recommended for opaque or solid samples, such as food dyes in powdered form. Transmittance color measurement mode is typically used for food dyes that are in liquid form and is transparent or translucent.
Konica Minolta Spectrophotometer for Food Dyes Color Measurement
The Konica Minolta Spectrophotometer CM-5 is a stand-alone color measurement instrument that is capable of performing both reflectance and transmittance color measurement, offering greater versatility in measuring the color of a wider range of food dyes. With a wide selection of accessories available, the spectrophotometer CM-5 can handle and provide a more comprehensive and accurate color measurement of food dyes ranging from powder and paste to liquid or from small to large volumes. The spectrophotometer CM-5 capability is further enhanced with the SpectraMagic NX color management software, allowing users to create custom color formulas intended for their specific needs. Check out this video to gain a better understanding of the various capabilities of the spectrophotometer CM-5.

Reflectance (left) and transmittance (right) color measurement with Spectrophotometer CM-5.
Interested in learning more about how to measure the color of food dyes or perhaps need help finding the right color measurement instrument for your application? Contact us today to schedule a free consultation with our experts and find out how we can help.
